One of a family of thin T × I triangulations that typically appear at the centres of layered torus bundles.
More...
#include <subcomplex/txicore.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| TxIDiagonalCore (size_t size, size_t k) | |
Creates a new T × I triangulation with the given parameters. | |
| TxIDiagonalCore (const TxIDiagonalCore &)=default | |
Creates a new copy of the given T × I triangulation. | |
| TxIDiagonalCore (TxIDiagonalCore &&) noexcept=default | |
Moves the contents of the given T × I triangulation into this new triangulation. | |
| TxIDiagonalCore & | operator= (const TxIDiagonalCore &src)=default |
Sets this to be a copy of the given T × I triangulation. | |
| TxIDiagonalCore & | operator= (TxIDiagonalCore &&src) noexcept=default |
Moves the contents of the given T × I triangulation into this triangulation. | |
| size_t | size () const |
Returns the total number of tetrahedra in this T × I triangulation. | |
| size_t | k () const |
| Returns the additional parameter k as described in the class notes. | |
| void | swap (TxIDiagonalCore &other) noexcept |
Swaps the contents of this and the given T × I triangulation. | |
| bool | operator== (const TxICore &other) const override |
Determines if this and the given T × I triangulation are of the same type and have the same parameters. | |
| std::ostream & | writeName (std::ostream &out) const override |
Writes the name of this specific triangulation of T × I to the given output stream. | |
| std::ostream & | writeTeXName (std::ostream &out) const override |
Writes the name of this specific triangulation of T × I in TeX format to the given output stream. | |
| const Triangulation< 3 > & | core () const |
Returns a full copy of the T × I triangulation that this object describes. | |
| size_t | bdryTet (int whichBdry, int whichTri) const |
| Determines which tetrahedron provides the requested boundary triangle. | |
| Perm< 4 > | bdryRoles (int whichBdry, int whichTri) const |
| Describes which tetrahedron vertices play which roles in the upper and lower boundary triangles. | |
| const Matrix2 & | bdryReln (int whichBdry) const |
| Returns a 2-by-2 matrix describing the α and β curves on a torus boundary in terms of specific tetrahedron edges. | |
| const Matrix2 & | parallelReln () const |
| Returns a 2-by-2 matrix describing the parallel relationship between the upper and lower boundary curves. | |
| std::string | name () const |
Returns the name of this specific triangulation of T × I as a human-readable string. | |
| std::string | texName () const |
Returns the name of this specific triangulation of T × I in TeX format. | |
| void | writeTextShort (std::ostream &out) const |
| Writes a short text representation of this object to the given output stream. | |
| void | writeTextLong (std::ostream &out) const |
| Writes a detailed text representation of this object to the given output stream. | |
| std::string | str () const |
| Returns a short text representation of this object. | |
| std::string | utf8 () const |
| Returns a short text representation of this object using unicode characters. | |
| std::string | detail () const |
| Returns a detailed text representation of this object. | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| void | swapBaseData (TxICore &other) noexcept |
| Swaps all data that is managed by this base class with the given triangulation. | |
Protected Attributes | |
| Triangulation< 3 > | core_ |
A full copy of the T × I triangulation that is described. | |
| std::array< std::array< size_t, 2 >, 2 > | bdryTet_ |
| The tetrahedra that provide the upper and lower boundary triangles. | |
| std::array< std::array< Perm< 4 >, 2 >, 2 > | bdryRoles_ |
| Describes which tetrahedron vertices play which roles in the upper and lower boundary triangles. | |
| std::array< Matrix2, 2 > | bdryReln_ |
| Expresses the α and β curves for each torus boundary in terms of specific tetrahedron edges and vertices. | |
| Matrix2 | parallelReln_ |
| Expresses the lower α and β curves in terms of the upper α and β curves. | |
Detailed Description
One of a family of thin T × I triangulations that typically appear at the centres of layered torus bundles.
Different triangulations in this family use different numbers of tetrahedra, with the larger triangulations producing more complicated relationships between the upper and lower boundary curves.
Members of this family are parameterised by their size (the number of tetrahedra) and an additional integer k, where 1 ≤ k ≤ size - 5. Note that this means we must have size ≥ 6. The member of this family of size n with additional parameter k is labelled T_n:k.
It is worth noting that T_n:k is isomorphic to T_n:(n-4-k), so in reality there are only [(n-4)/2] different triangulations for a given size (rounded down).
A triangulation of this family is most easily defined in terms of its central torus. Central surfaces are described in detail in "Structures of small closed non-orientable 3-manifold triangulations", Benjamin A. Burton, J. Knot Theory Ramifications 16 (2007), 545–574; in particular, see the section on thin I-bundles.
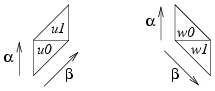
The central torus begins with two triangles u0 and u1 (which eventually provide the upper torus boundary), with a chain of quadrilaterals q1, ..., q(n-5) descending diagonally beneath them as illustrated in the diagram below.

We then distort quadrilateral qk and attach two more triangles w0 and w1 to its side (these will eventually provide the lower torus boundary). This is illustrated in the following diagram.

The entire central torus wraps from left to right (so the lower left edges of most quadrilaterals qi are identified with the upper right edges of q(i-1), and the left edge of qk is identified with the right edge of w1). As an exception, the two uppermost edges are identified with the two lowermost edges in a parallel fashion (so the upper left edge of u1 is identified with the lower right edge of q1, and the adjacent edges at right angles to these are also identified).
The four triangles in the central torus correspond to the four tetrahedra in the triangulation that provide the boundary triangles. The upper boundary is coned out from triangles u0 and u1, and the lower boundary is coned out from triangles w0 and w1. In each boundary, u0 or w0 gives the first boundary triangle and u1 or w1 gives the second. The directions of the corresponding α and β curves are illustrated below.
As a final illustration, the example below shows the central surface in the case (n, k) = (9, 2).

This class implements C++ move semantics and adheres to the C++ Swappable requirement. It is designed to avoid deep copies wherever possible, even when passing or returning objects by value.
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
◆ TxIDiagonalCore() [1/3]
| regina::TxIDiagonalCore::TxIDiagonalCore | ( | size_t | size, |
| size_t | k ) |
Creates a new T × I triangulation with the given parameters.
- Parameters
-
size the number of tetrahedra in this triangulation. This must be at least 6. k the additional parameter k as described in the class notes. This must be between 1 and (size - 5) inclusive.
◆ TxIDiagonalCore() [2/3]
|
default |
Creates a new copy of the given T × I triangulation.
◆ TxIDiagonalCore() [3/3]
|
defaultnoexcept |
Moves the contents of the given T × I triangulation into this new triangulation.
The triangulation that was passed will no longer be usable.
Member Function Documentation
◆ bdryReln()
|
inlineinherited |
Returns a 2-by-2 matrix describing the α and β curves on a torus boundary in terms of specific tetrahedron edges.
Consider the first triangle of the given boundary. Let t be the tetrahedron returned by bdryTet(whichBdry, 0) and let p be the permutation returned by bdryRoles(whichBdry, 0).
Let edge01 be the directed edge from vertex p[0] to p[1] of tetrahedron t, and let edge02 be the directed edge from vertex p[0] to p[2] of tetrahedron t. Then the matrix returned by this routine describes how the directed edges edge01 and edge02 relate to the α and β curves on the given boundary. Specifically:
[ α ] [ edge01 ]
[ ] = bdryReln() * [ ] .
[ β ] [ edge02 ]
It is guaranteed that this matrix has determinant +1 or -1.
- Parameters
-
whichBdry 0 if the upper boundary should be examined, or 1 if the lower boundary should be examined.
- Returns
- the relationship between the boundary curves and tetrahedron edges.
◆ bdryRoles()
|
inlineinherited |
Describes which tetrahedron vertices play which roles in the upper and lower boundary triangles.
Each boundary torus contains two triangles, whose vertices can be numbered 0, 1 and 2 according to the following diagram. This diagram is completely symmetric, in that edges 1-2 are no more special than edges 0-2 or 0-1. The important observations are that edges 1-2 and 2-1 of each triangle are identified, edges 0-2 and 2-0 of each triangle are identified and edges 0-1 and 1-0 of each triangle are identified.
*--->>--*
|0 2 / |
First | / 1| Second
triangle v / v triangle
|1 / |
| / 2 0|
*--->>--*
This routine returns a permutation that maps these integers 0,1,2 to real tetrahedron vertices. Let t be the tetrahedron returned by bdryTet(whichBdry, whichTri) and let p be the permutation returned by bdryRoles(whichBdry, whichTri). Then vertices p[0], p[1] and p[2] of tetrahedron t correspond to the markings 0, 1 and 2 respectively in the diagram above (and therefore the boundary triangle is face p[3] of the tetrahedron).
The arguments to this routine affect whether we examine the upper or lower boundary and whether we examine the first or second triangle of this boundary
- Parameters
-
whichBdry 0 if the upper boundary should be examined, or 1 if the lower boundary should be examined. whichTri 0 if the first boundary triangle should be examined, or 1 if the second boundary triangle should be examined.
- Returns
- the permutation mapping roles 0, 1 and 2 in the diagram above to real tetrahedron vertex numbers.
◆ bdryTet()
|
inlineinherited |
Determines which tetrahedron provides the requested boundary triangle.
Recall that the T × I triangulation has two torus boundaries, each consisting of two boundary triangles. This routine returns the specific tetrahedron that provides the given triangle of the given torus boundary.
What is returned is the index number of the tetrahedron within the triangulation. To access the tetrahedron itself, you may call core().tetrahedron(bdryTet(...)).
Note that the same tetrahedron may provide more than one boundary triangle.
- Parameters
-
whichBdry 0 if the upper boundary should be examined, or 1 if the lower boundary should be examined. whichTri 0 if the first boundary triangle should be examined, or 1 if the second boundary triangle should be examined.
◆ core()
|
inlineinherited |
Returns a full copy of the T × I triangulation that this object describes.
Successive calls to this routine will return a reference to the same triangulation (i.e., it is not recreated each time this function is called).
- Returns
- the full triangulation.
◆ detail()
|
inherited |
Returns a detailed text representation of this object.
This text may span many lines, and should provide the user with all the information they could want. It should be human-readable, should not contain extremely long lines (which cause problems for users reading the output in a terminal), and should end with a final newline. There are no restrictions on the underlying character set.
- Returns
- a detailed text representation of this object.
◆ k()
|
inline |
Returns the additional parameter k as described in the class notes.
- Returns
- the additional parameter k.
◆ name()
|
inherited |
Returns the name of this specific triangulation of T × I as a human-readable string.
- Returns
- the name of this triangulation.
◆ operator=() [1/2]
|
default |
Sets this to be a copy of the given T × I triangulation.
This will induce a deep copy.
- Returns
- a reference to this triangulation.
◆ operator=() [2/2]
|
defaultnoexcept |
Moves the contents of the given T × I triangulation into this triangulation.
The triangulation that was passed will no longer be usable.
- Returns
- a reference to this triangulation.
◆ operator==()
|
inlineoverridevirtual |
Determines if this and the given T × I triangulation are of the same type and have the same parameters.
If this returns true, then the triangulations returned by core() should also be combinatorially identical.
- Parameters
-
other the T × Itriangulation to compare with this.
- Returns
trueif and only if this and the given triangulation are of the same type and have the same parameters.
Implements regina::TxICore.
◆ parallelReln()
|
inlineinherited |
Returns a 2-by-2 matrix describing the parallel relationship between the upper and lower boundary curves.
Let a_u and b_u be the upper α and β boundary curves. Suppose that the lower α is parallel to w.a_u + x.b_u, and that the lower β is parallel to y.a_u + z.b_u. Then the matrix returned will be
[ w x ]
[ ] .
[ y z ]
In other words, if a_l and b_l are the lower α and β curves respectively, we have
[ a_l ] [ a_u ]
[ ] = parallelReln() * [ ] .
[ b_l ] [ b_u ]
- Returns
- the relationship between the upper and lower boundary curves.
◆ size()
|
inline |
Returns the total number of tetrahedra in this T × I triangulation.
- Returns
- the total number of tetrahedra.
◆ str()
|
inherited |
Returns a short text representation of this object.
This text should be human-readable, should use plain ASCII characters where possible, and should not contain any newlines.
Within these limits, this short text ouptut should be as information-rich as possible, since in most cases this forms the basis for the Python __str__() and __repr__() functions.
- Python
- The Python "stringification" function
__str__()will use precisely this function, and for most classes the Python__repr__()function will incorporate this into its output.
- Returns
- a short text representation of this object.
◆ swap()
|
inlinenoexcept |
Swaps the contents of this and the given T × I triangulation.
- Parameters
-
other the triangulation whose contents should be swapped with this.
◆ swapBaseData()
|
protectednoexceptinherited |
Swaps all data that is managed by this base class with the given triangulation.
- Note
- This function is marked
noexcept, even though it calls Triangulation<3>::swap() which is notnoexcept. This is because the only potential cause of exceptions comes from packet event listeners, and the internal triangulation here does not belong to a packet.
- Parameters
-
other the triangulation whose data should be swapped with this.
◆ texName()
|
inherited |
Returns the name of this specific triangulation of T × I in TeX format.
No leading or trailing dollar signs will be included.
- Returns
- the name of this triangulation in TeX format.
◆ utf8()
|
inherited |
Returns a short text representation of this object using unicode characters.
Like str(), this text should be human-readable, should not contain any newlines, and (within these constraints) should be as information-rich as is reasonable.
Unlike str(), this function may use unicode characters to make the output more pleasant to read. The string that is returned will be encoded in UTF-8.
- Returns
- a short text representation of this object.
◆ writeName()
|
inlineoverridevirtual |
Writes the name of this specific triangulation of T × I to the given output stream.
The name will be written as a human-readable string.
- Python
- Not present. Instead use the variant name() that takes no arguments and returns a string.
- Parameters
-
out the output stream to which to write.
- Returns
- a reference to the given output stream.
Implements regina::TxICore.
◆ writeTeXName()
|
inlineoverridevirtual |
Writes the name of this specific triangulation of T × I in TeX format to the given output stream.
No leading or trailing dollar signs will be written.
- Python
- Not present. Instead use the variant texName() that takes no arguments and returns a string.
- Parameters
-
out the output stream to which to write.
- Returns
- a reference to the given output stream.
Implements regina::TxICore.
◆ writeTextLong()
|
inlineinherited |
Writes a detailed text representation of this object to the given output stream.
- Python
- Not present. Use detail() instead.
- Parameters
-
out the output stream to which to write.
◆ writeTextShort()
|
inlineinherited |
Writes a short text representation of this object to the given output stream.
- Python
- Not present. Use str() instead.
- Parameters
-
out the output stream to which to write.
Member Data Documentation
◆ bdryReln_
|
protectedinherited |
Expresses the α and β curves for each torus boundary in terms of specific tetrahedron edges and vertices.
The elements bdryReln_[0] and bdryReln_[1] refer to the upper and lower boundaries respectively, and each of these matrices must have determinant ±1. See bdryReln() for further details.
◆ bdryRoles_
|
protectedinherited |
Describes which tetrahedron vertices play which roles in the upper and lower boundary triangles.
See bdryRoles() for details.
◆ bdryTet_
|
protectedinherited |
The tetrahedra that provide the upper and lower boundary triangles.
See bdryTet() for details.
◆ core_
|
protectedinherited |
A full copy of the T × I triangulation that is described.
◆ parallelReln_
|
protectedinherited |
Expresses the lower α and β curves in terms of the upper α and β curves.
See parallelReln() for details.
The documentation for this class was generated from the following file:
- subcomplex/txicore.h
Copyright © 1999–2025, The Regina development team